- Data Binding - Angular JS provides two way binding is automatic synchronization of the data between model and view.
- Extensible - AngularJS is customized and extensible . Allows you to create customizable components.
- Code Reusability and Maintainability - AngularJS forces you to write code in modular way. Variables and functions can only be created to the respective component(Controller). Provides service and factory implemetation to use across the controllers.
- Compatibility - AngularJS is compatible to all major browsers
- Testing - AngularJS is designed to be testable so that you can test your AngularJS app components as easy as possible. It has dependency injection at its core, which makes it easy to test.
Saturday, June 20, 2015
Advantages of Angular JS
Tuesday, June 16, 2015
Angular JS Services
- In Angular, Services are the business logic can be shared across the controllers.
- Services needs to be injected(dependency injection) to make use of it in any component.
- Services instantiates only when component demands (Lazy instantiation).
- Services are Singleton, single reference shared across the components.
- Services can have their own dependencies similar declaring dependencies in a controller.
<body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="myController"> {{message}} <br />
<input type="text" ng-model="sqr" ng-init="sqr=5"> Square of <b>{{sqr}}</b> = {{squareCtrl(sqr)}}
</div>
</body>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
// Service logger to log
myApp.factory("logger", function() {
return function(v) {
console.log(v);
}
});
// Square service for square arithmetic operation
myApp.factory("square", [ "logger", function(logger) {
return function(v) {
// Service looger dependency injected to this service
logger("Square root for : " + v);
return v * v;
}
}]);
myApp.controller('myController', ['$scope', 'square', function($scope, square) {
//Property to the scope
$scope.message = 'Hello!';
//Behaviour to the scope
$scope.squareCtrl = function(v) {
return square(v);
};
}]);
</script>
Monday, June 15, 2015
Angular JS - Nested Controllers
- In HTML DOM can be created in hierarchy(Parent and child DOM elements).
- Same way, Angular JS controllers also attached to the DOM hierarchy.
- Obviously these are the Nested controllers.
- The variable $scope will be created for the respective controller.
- Intresting point here is, The $scope variable will have the access to the properties and methods to the higher $scope hierarchy.
Nested Controllers
<div ng-controller="ParentController" ng-app="nestedControllers"><p>{{prefix}} {{ctrl}}</p>
<div ng-controller="ChildController">
<p>{{prefix}} {{ctrl}}</p>
<div ng-controller="GrandChildController">
<p>{{prefix}} {{ctrl}}</p>
</div>
</div>
$scope hierarchy
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('nestedControllers', []);
myApp.controller('ParentController', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.ctrl = 'ParentController';
$scope.prefix = 'I am'; //overrides in the child controllers
}]);
myApp.controller('ChildController', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.ctrl = 'ChildController';
}]);
myApp.controller('GrandChildController', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.ctrl = 'GrandChildController';
}]);
</script>
Angular JS - Controllers
- In Angular JS Controller is the Javascript constructor function.
- When directive ng-controller is added to the DOM, Angular create a constructor function to the controller.
- And creates variable $scope to the respective controller.
<body ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="myController"> {{message}} <br />
<input type="text" ng-model="sqr" ng-init="sqr=5"> Square of <b>{{sqr}}</b> = {{square(sqr)}}
</div>
</body>
<script>
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp.controller('myController', ['$scope', function($scope) {
//Property to the scope
$scope.message = 'Hello!';
//Behaviour to the scope
$scope.square = function(v) {
return v * v;
};
}]);
</script>
Sunday, June 14, 2015
Angular JS Data Binding
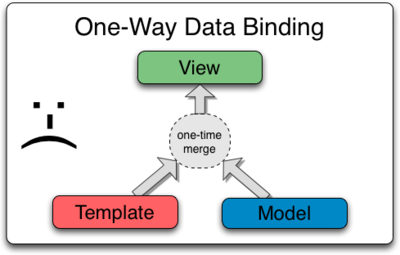 | ||
Traditional One Way Binding |
AngularJS Concetps
| Please find the following significant concepts of the Angular JS | |
|---|---|
1. Template |
| HTML acts as the template engine with additional markups. |
2. Directives |
| Extends the HTML DOM with the custom attributes . |
3.Model |
| The values that are stored in variables on the scope are referred to as the model |
4.Scope |
| Block or context in the HTML. So that Model is stored where controllers and directives can access it. |
5.Expressions |
| An expression in a template is a JavaScript-like code snippet that allows to read and write variables. Note that those variables are not global variables. Just like variables in a JavaScript function live in a scope, |
6.Compiler |
| When Angular starts your application, it parses and processes this new markup from the template using the compiler. |
7.Filter |
| A filter formats the value of an expression for display to the user |
8.View |
| The loaded, transformed and rendered DOM is then called the view. |
9.Data Binding |
| Whenever the input values change, the value of the expressions are automatically recalculated and the DOM is updated with their values. The concept behind this is two-way data binding. |
10.Controller |
| Business logic behind views. The purpose of controllers is to expose variables and functionality to expressions and directives. |
11.Dependency Injection |
| Creates and wires objects and functions |
12.Injector |
| Dependency Injection (DI) is a software design pattern that deals with how objects and functions get created and how they get a hold of their dependencies. Everything within Angular (directives, filters, controllers, services, ...) is created and wired using dependency injection. Within Angular, the DI container is called the injector. |
13.Module |
| To use Dependency Injection, there needs to be a place where all the things that should work together are registered. In Angular JS, this is the purpose of the modules. |
14.Service |
| View-independent logic from the controller into a service, so it can be reused by other parts of the application as well. Can be accessed from the different controllers. |
Saturday, June 13, 2015
AngularJS - Hello World
Angular JS is a javascript opensource powerful framework.
Angular JS provides us the efficient way to create Single Page Application (SPA).
Angulars JS lets you to extend traditional HTML.
Extensible and works well with the other libraries.
MVC WAY
- Angular JS helps you to write clean MVC (Model View Controller) Javascript code.
- It uses HTML has the template language, by extending the DOM attributes.
Angular JS Hello World
Like any other framework Angular JS also needs to be added in the script tag src<head>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.2.5/angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
ng-app
Tells the framework that the HTML block is Angular application.
<body ng-app="myapp" ></body>
ng-model
Intended to be put inside of form elements and has two-way data binding ($scope -> view and view -> $scope)
<input type="text" ng-model="uname" >
{{ }} Declaration
Specifying the Angular JS variables inside the HTML tags.
<h1>{{ uname }}</h1>
Hello World
- <!doctype html>
- <html
ng-app> - <head>
- <script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.16/
angular.min.js"></script> - </head>
- <body>
- <div>
- <label>Name:</label>
- <input type="text"
ng-model="uname" placeholder="Enter a your name"> - <hr>
- <h1>Hello
{{uname}}!</h1> - </div>
- </body>
- </html>
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Serverless vs. Kubernetes: A Beginner's Guide
Serverless vs. Kubernetes: A Beginner's Guide Trying to decide between serverless and Kubernetes? Here's a simple breakdown: 🔹 Choo...
-
In Javascript world the things are always confused. The most confused and made complicated feature is closure. But the truth is Javascrip...
-
Javascript prototype is quite fuzzy word for javascript developers in the beginning. Prototype is the property which is available for all...
-
Ext.defer or Ext.function.defer is a function similar to javascript setTimeout function. Ext. defer (function() { alert('H...



