Angular JS is a javascript opensource powerful framework.
Angular JS provides us the efficient way to create Single Page Application (SPA).
Angulars JS lets you to extend traditional HTML.
Extensible and works well with the other libraries.
MVC WAY
- Angular JS helps you to write clean MVC (Model View Controller) Javascript code.
- It uses HTML has the template language, by extending the DOM attributes.
Angular JS Hello World
Like any other framework Angular JS also needs to be added in the script tag src
<head>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.2.5/angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
ng-app
Tells the framework that the HTML block is Angular application.
<body ng-app="myapp" ></body>
ng-model
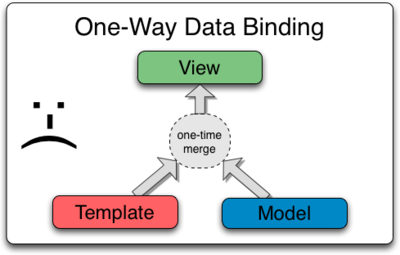
Intended to be put inside of form elements and has two-way data binding ($scope -> view and view -> $scope)
<input type="text" ng-model="uname" >
{{ }} Declaration
Specifying the Angular JS variables inside the HTML tags.
<h1>{{ uname }}</h1>
Hello World
- <!doctype html>
- <html
ng-app>
- <head>
- <script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.16/
angular.min.js"></script>
- </head>
- <body>
- <div>
- <label>Name:</label>
- <input type="text"
ng-model="uname" placeholder="Enter a your name">
- <hr>
- <h1>Hello
{{uname}}!</h1>
- </div>
- </body>
- </html>